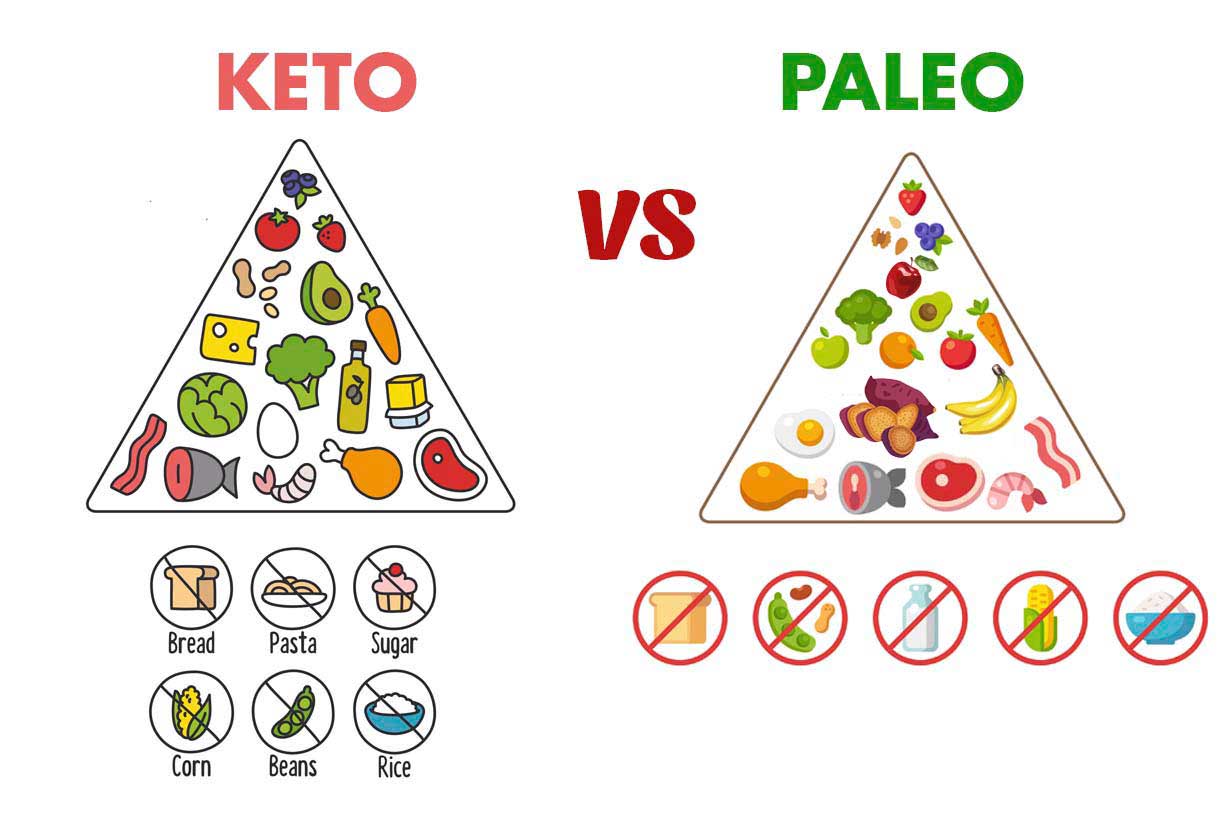
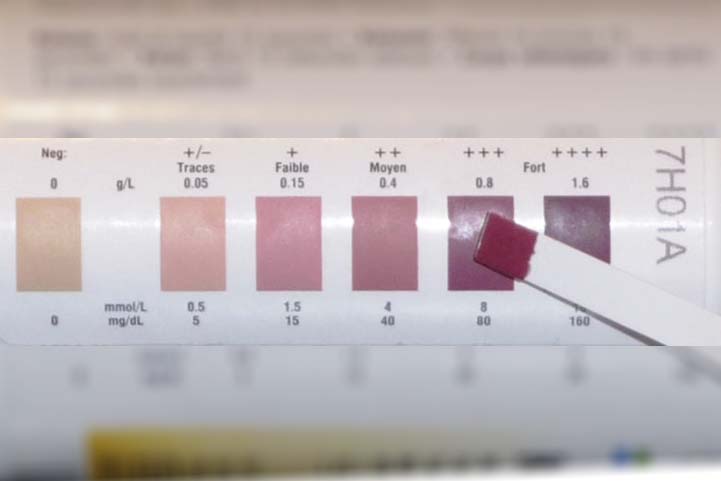
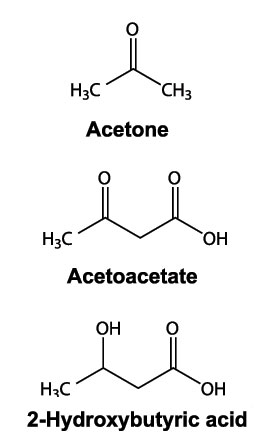
With frequent coverage in the media, low carb and ketogenic diets have become increasingly popular over recent years.
But what do all these different terms like ketogenesis and ketone bodies actually mean?
This article provides a short summary of what the ketogenesis pathway is and what ketone bodies do.
What is Ketogenesis?
Ketogenesis is a biochemical process through which the body breaks down fatty acids into ketone bodies (1).
Synthesis of ketone bodies through ketogenesis kicks in during times of carbohydrate restriction or periods of fasting. When carbohydrate is in short supply, ketones become the default energy source for our body (1).
Ketogenesis may also occur at slightly higher levels of carbohydrate intake. When ketogenesis takes place, the body produces ketone bodies as an alternative fuel to glucose.
This physiological state is known as ‘nutritional ketosis’.
There are various methods people can use to test if they are “in ketosis”.
It is also worth noting that ‘ketosis’ and ‘ketoacidosis’ are very different things. For more on this topic, see this guide to how ketoacidosis relates to a ketogenic diet.
What Are Ketone Bodies?
Ketone bodies are water-soluble compounds that act as a form of energy in the body.
There are three major types of ketone body (2):
- Acetoacetate
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate
- Acetone (a compound created through the breakdown of acetoacetate)
As an alternative energy source to glucose, these ketones can also satisfy our body’s energy requirements.
However, unlike glucose, ketone bodies do not impact blood sugar or insulin levels.
Related Articles