Arginine is an amino acid that plays a range of important functions in the body.
This article provides a list of foods high in arginine alongside an overview of why arginine is important.
Before we explore the richest dietary sources, let’s first take a look at what arginine is.
What Is Arginine?
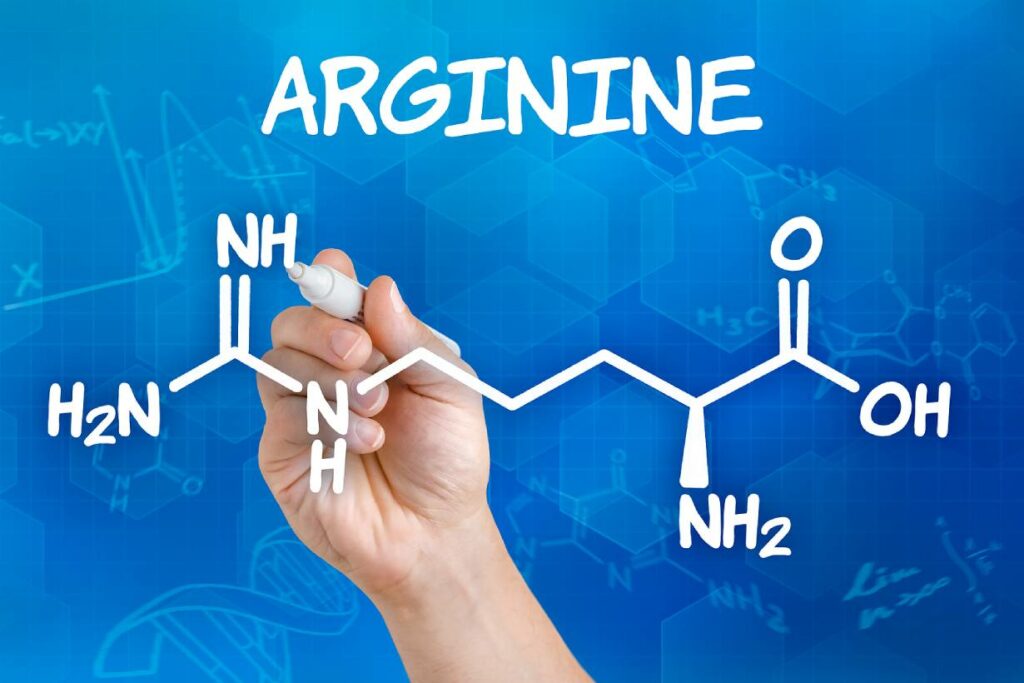
Arginine, also known as L-arginine, is an amino acid used by the body to make protein.
Some amino acids are deemed essential, meaning that the body cannot produce them and requires them from the diet.
Conversely, certain amino acids are considered ‘non-essential’ since the body can produce them internally.
In the case of arginine, this amino acid has the distinctive class of a ‘conditionally essential’ amino acid (1, 2).
Although the body can produce it, there are specific circumstances in which the body may require additional arginine from the diet.
This is because, at times, the body’s arginine requirements may be higher than the amount it can produce. Some instances where we may require extra arginine include (3, 4):
- Injury, illness, and certain diseases: The body uses arginine for recovery and wound healing. Specific conditions may increase arginine requirements or lower the body’s endogenous (internal) production of it.
- Growth: Arginine plays a key role in the growth and development of children and teenagers.
- During pregnancy: Arginine requirements increase during pregnancy to help the growth of the developing baby.
- After exercise: Arginine needs are higher when following a heavy exercise program. Arginine plays a role in performance and recovery as it is a precursor to nitric oxide, which is involved in blood flow regulation.
How Can We Get Enough Arginine?
Most individuals typically consume a sufficient amount of arginine from their daily diet.
Given that most protein-rich foods have a high arginine content, maintaining a sufficient protein intake throughout the day should ensure a sufficient arginine intake.
Foods such as meat, seafood, legumes, and nuts all tend to be high in arginine.
Foods High In Arginine
In descending order, arranged according to serving size, here are the richest dietary sources of arginine.
1) Whelk, cooked
Whelk, a nutrient and protein-rich sea snail, provides 4.2 grams of arginine per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (5).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) serving |
|---|---|
| 4.94 grams | 4.2 grams |
2) Chicken breast, skinless, cooked
Chicken breast is widely recognized as one of the best dietary sources of protein, and it boasts high levels of arginine.
A large (196-gram) cooked chicken breast offers 4.04 grams of the amino acid (6).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per large (196g) piece |
|---|---|
| 2.06 grams | 4.04 grams |
3) Soy flour, defatted
As soy is naturally high in protein, defatted flour, containing more protein and less fat, has a higher amino acid content.
A 106-gram cup of soy flour contains 3.83 grams of arginine (7).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 106g cup |
|---|---|
| 3.65 grams | 4.04 grams |
4) Peanut flour, defatted
Defatted peanut flour is another arginine-rich flour option. It contains 3.74 grams per 60-gram cup (8).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 60g cup |
|---|---|
| 6.24 grams | 3.61 grams |
5) Whitefish, dried
Dried whitefish is typically used as a portable, protein-rich snack.
It has an arginine content of 3.61 grams per 100 grams (9).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 100g |
|---|---|
| 3.61 grams | 3.61 grams |
6) Pork chop, lean only, cooked
A lean pork chop has a higher amino acid content per gram compared to fattier cuts.
A 219-gram pork chop offers 3.53 grams of arginine (10).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 219g chop |
|---|---|
| 1.61 grams | 3.53 grams |
7) Sunflower seed flour, partially defatted
Partially defatted sunflower seed flour, due to its reduced fat content, offers a higher concentration of protein and amino acids, including arginine.
A 64-gram serving provides 3.24 grams of arginine (11).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 64g cup |
|---|---|
| 5.07 grams | 3.24 grams |
8) Lupin beans, cooked
Lupin beans are among the richest protein legumes, thus they contain a notable concentration of amino acids.
Each 166-gram cup of cooked lupin beans has 2.77 grams of arginine (12).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 64g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.67 grams | 2.77 grams |
9) Lobster (Northern), cooked
A 145-gram cup of cooked Northern lobster offers an arginine content of 2.54 grams (13).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 145g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.75 grams | 2.54 grams |
10) Cod, cooked
Cod, a lean white fish rich in amino acids, supplies 2.47 grams of arginine per 180-gram fillet (14).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 64g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.37 grams | 2.77 grams |
11) Halibut, cooked
Halibut, another arginine-rich white fish, offers 2.4 grams of the amino acid per 159-gram half-fillet (15).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 159g half-fillet |
|---|---|
| 1.51 grams | 2.4 grams |
12) Crab, blue, cooked
Blue crab is among the most arginine-rich shellfish, providing 2.38 grams per cup (135g) serving (16).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 135g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.76 grams | 2.38 grams |
13) Rockfish, cooked
A 149-gram fillet of cooked rockfish has an arginine content of 2.26 grams (17).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 149g fillet |
|---|---|
| 1.52 grams | 2.26 grams |
14) Soybeans, cooked
As a high-protein legume, soybeans are one of the best plant-based sources of arginine. A 172-gram cup serving supplies 2.22 grams (18).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 172g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.29 grams | 2.22 grams |
15) Haddock, cooked
Haddock, a lean fish with considerable protein content, delivers 2.07 grams of arginine per 150g fillet (19).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 150g fillet |
|---|---|
| 1.38 grams | 2.07 grams |
16) Cuttlefish, cooked
A three-ounce (85-gram) serving of cuttlefish provides 2.01 grams of arginine (20).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) |
|---|---|
| 2.37 grams | 2.01 grams |
17) Shrimp, cooked
Shrimp offers a good source of arginine, with 1.91 grams per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (21).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) |
|---|---|
| 2.25 grams | 1.91 grams |
18) Soy protein isolate
As an almost purely protein source, soy protein isolate is mainly used for making protein shakes.
Just an ounce (28.35g) serving contains 1.89 grams of arginine (22).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per ounce (28.35g) |
|---|---|
| 6.67 grams | 1.89 grams |
19) Gelatin powder, unsweetened
Unsweetened gelatin powder is a concentrated source of arginine, supplying 1.85 grams per ounce (28.35g) package (23).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per ounce (28.35g) package |
|---|---|
| 6.62 grams | 1.85 grams |
20) Chicken drumstick
A chicken drumstick, typically weighing 105 grams with the skin, provides 1.74 grams of arginine (24).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 105-gram drumstick |
|---|---|
| 1.66 grams | 1.74 grams |
21) Tofu, firm
Per half cup (126-gram) serving, firm tofu typically supplies 1.73 grams of arginine (25).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 126-gram half-cup |
|---|---|
| 1.37 grams | 1.73 grams |
22) Turkey, ground, cooked
With 1.69 grams of arginine per three-ounce (85-gram) serving, ground turkey offers a substantial amount of the amino acid (26).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) serving |
|---|---|
| 1.99 grams | 1.69 grams |
23) Beef, top sirloin, cooked
Top sirloin is one of the highest-arginine cuts of beef, providing 1.67 grams per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (27).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) serving |
|---|---|
| 1.96 grams | 1.67 grams |
24) Clams, mixed species, cooked
Clams are another arginine-rich shellfish, supplying 1.58 grams of the amino acid per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (28).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) serving |
|---|---|
| 1.86 grams | 1.58 grams |
25) Pork tenderloin, lean only, cooked
Lean pork tenderloin has an arginine content of 1.48 grams per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (29).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 3oz (85g) serving |
|---|---|
| 1.74 grams | 1.48 grams |
26) Lentils, cooked
Lentils are another plant-based source of arginine, with a cup serving providing 1.38 grams (30).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 198g cup |
|---|---|
| 0.70 grams | 1.38 grams |
27) Chickpeas, cooked
Each 164-gram cup of cooked chickpeas offers approximately 1.37 grams of arginine (31).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 164g cup |
|---|---|
| 0.84 grams | 1.37 grams |
28) Crayfish, cooked
On average, crayfish supply around 1.3 grams of arginine per three-ounce (85-gram) serving (32).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 164g cup |
|---|---|
| 1.53 grams | 1.30 grams |
29) Cottage cheese, lowfat, 1% milkfat
Low-fat cottage cheese has less fat and more protein (thus amino acids) than regular varieties.
A 226-gram cup of low-fat cottage cheese offers 1.28 grams of arginine (33).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 226g cup |
|---|---|
| 0.57 grams | 1.28 grams |
30) Broad beans (fava beans), cooked
Fava beans, also known as broad beans, are a good source of arginine, providing 1.19 grams per 170-gram cup serving (34).
| Arginine per 100 grams | Arginine per 170g cup |
|---|---|
| 0.70 grams | 1.19 grams |
Is Arginine Supplementation Beneficial?
In addition to arginine-rich foods, it is possible to purchase arginine supplements.
Firstly, as mentioned earlier, the majority of individuals obtain sufficient arginine from their daily diet and are unlikely to significantly benefit from supplementation.
That said, arginine supplementation may have potential benefits for certain individuals.
For example, arginine is a precursor for nitric oxide, so higher intakes may enhance nitric oxide production (35). Nitric oxide helps to dilate blood vessels, thus improving blood flow, which could potentially improve performance for intense exercise and physical activities.
Some studies show potential performance benefits from arginine supplementation, but the data is inconsistent, showing mixed results (36, 37).
Furthermore, research has also demonstrated that arginine supplementation might be effective for lowering blood pressure (38, 39).
However, as Mayo Clinic states, “because they can affect how some medicines work and worsen certain health conditions, they (arginine supplements) shouldn’t be taken unless a healthcare professional recommends them” (38).
Anyone considering arginine supplementation should discuss the matter with their primary healthcare provider beforehand.
Final Thoughts
Arginine is an important amino acid that is conditionally essential for human health.
However, the majority of people obtain sufficient amounts of arginine from their daily diet.
Arginine can be found in high concentrations in most animal-based proteins as well as protein-rich legumes, nuts, grains, and seeds.